
The Fundamental Unit of Life : cell
By: Ghanshyam kr. chaudhary.
CYTOLOGY: The branch of biology which deals with the systematic study of the structural composition of the cell.
Cell:
It is defined as the basic structural unit of the life of living organisms, whether they are unicellular or multicellular.
Therefore we can say that cell is the fundamental unit of life.
Discovery of the cell:
Cell is first discovered by Robert Hooke in a dead cork slice in the year 1665.
IInd Discovery of the cell:
A.V. Leeuwenhoek discovered first living cell in pond water in the year 1674.
Qus1. Who gave the theory of the cell?
Ans: Schleiden and Schwann gave the theory of the cell.
which states that :
- All plants and animals are composed of cells.
- Cell is the basic unit of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
- Viruses are the exceptions of cell theory.
Classification of organisms
organisms are classified on the basis of cell arrangement
Types of organism: Unicellular or multicellular.
Unicellular (Uni: one, cellular: cell )
The single - celled organisms are called unicellular organisms.
Example: Amoeba, Paramecium, etc.
Multicellular organisms (Multi: Many, cellular: cell )
Organisms which are made up of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms.
Example: Plants and higher animals.
Qus2. write the point of difference between plant and animal?
Ans: Plant cell
- The size of plant cell is large than animal cell.
- The shape and size of the plant cell is fixed.
- It contain cell wall made up of cellulose.
- Plastid are present in plant cell. ex.chloroplast.
- Plant cell contain large vacuoles.
- Animal cell is comparatively smaller than plant cell.
- It has no fixed shape and size.
- It is Lake from cell wall.
- Plastid are absent in animal cells plant.
- Animal cells contain vacuoles or less as compared to plant cell.
Qus3. what is the difference between prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell?
Ans: In prokaruotic cell
The three basic Components of the any cell is:
Cell membrane
The main function of the plasma membrane is are as follows:
1. Cytosol: The aqueous soluble part which contain protein forming cytoskeleton.
2. cell organelle: Living part of the cell having definite shape, structure and function eg. Mitochondria, Lysosomes, Nucleus, Ribosomes, etc.
Cell wall
The main function of Golgi apparatus is are as follows:
1. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
2. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Qus4. Write the difference between SER & RER?
Ans: SER (Smooth endoplasmic reticulum)
Ans: Membrane biogenesis is the process of synthesising cell membrane with the help of proteins and lipids. Endoplasmic reticulum(SER) is responsible for the synthesis of these membranes.
Ribosomes
Qus7.why lyososomes are called suicidal bag?( FAQs)
Ans: Because during metabolisms process cells get damaged and stop the metabolism process hence the lysosome break and release the hormone which digest their own dead cells. So it is called as Suicidal bag.
This process is referred as autolysis or self digestion.
Qus8. Defined the term autolysis?
Ans: It is defined as the process through which cell is destroyed by the action of its own enzymes.
Qus9. why lysosomes are called as digestive bag?
Ans: Because, they destroy the foreign materials such as bacteria and viruses when enter into the cell they digest them and protects the cell from viral and bacterial infection.
Vacuoles
The main function of vacuoles are as follows:
1.Leucoplast (white, found in underground parts)
2.Chromoplast(red, brown)
3.Chloroplast(Green in colour, found in aerial parts of plants & helps in photosynthesising. So it is called as the "kitchen of the plants")
Function
The main function of plastid are the following:
Diffusion
It is defined as the movement of solute(ions) particles from its high concentration to lower concentration is called diffusion.
Osmosis
It is defined as the movement of solute(ions) particles from its high concentration to lower concentration through Semi permeable membrane is called as osmosis.
It occurs only in liquid medium.
Osmosis require energy.
It is bidirectional.
Example. Movement of water in plant.
The movement of osmosis is two types:
1.Endomosis: The movement of solute/solvent particles from outside the cell to inside the cell is called as endomosis.
2.Exomosis: The movement of solute particles from inside to outside the cell is callesd as exomosis.
Qus11.Discuss the type of solution on the basis of concentration?
Ans: Types of solution on the basis of concentration
1.Isotonic solution
It occurs when the concentration of the solution is equal to the concentration of the cell. Due to this, no change will occur in the cell.
Isotonic solution: concentration of solution = concentration of the cell.
Result: No change will observe in the shape of the cell.
2.Hypertonic solution
It occur when the Concentration of the solution is greater than the concentration of the cell cytoplasm. Due to this, cell will shrink.
Hypertonic solution: Concentration of solution > Cell concentration
Result: Cell get shrink or
plasmolysed.
3.Hypotonic solution
It occurs when the concentration of the solution is lower than the concentration of the cell cytoplasm. As the result, cell swell up and may be burst.
Hypotonic solution: Concentration of solution < cell concentration.
Result: Cell will swells up & may be brust.
Qus12.What do you mean by plasmolysed cell?
Ans: Plasmolysed cell means, cell which get shrink due to the looses of water. It occur when cell is kept in a hypertonic solution in which the concentration of the solution is greater than the concentration of cell cytoplasm.
Qus13. What will happened when a eukaryotic cell is placed in a isotonic, hypertonic & hypotonic solution respectively?
Ans: When a eukaryotic cell is kept in isotonic solution, their is no changes will observed on the cell.
But cell will swells up when it kept in hypotonic solution and it may bursts.
similarly when is kept in hypertonic solution it will looses the water molecules and gets plasmolysed.
Ans: In prokaruotic cell
( 1 - 10 nm )
- Size of the cell is comparatively small.
- Nucleus is absent.
- cell division is occurs by either budding or fission i.e mitosis is absent.
- Membrane bound cell organelles are absent.
- Example : Bacteria and blue green algae.
- Size of the cell is larger.
- Nucleus is present.
- Cell division occur by either meiosis and Mitosis.
- Membrane bound cell organelles are present.
- Example: Fungi, plant and animal cells.
The three basic Components of the any cell is:
- Plasma membrane
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm.
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome,
- Plastid,
- Vacuoles,
- Peroxisomes &
- Centrosomes.
Cell membrane
- It is also known as plasma membrane or plasma lemma.
- cell membrane (plasma membrane) present in both plant and animal cell.
- ( Note: In plant cell, plasma membrane lies below the cell wall while in animal cell it is outermost covering of the cell. )
- Plasma membrane is made up of proteins and lipids.
- plasma membrane have selectively permeable in nature i.e it allow to move the solvent particle inside and outside the cell.
The main function of the plasma membrane is are as follows:
- As the cell membrane is SPM in nature, therefore it allow to move the waste solvent particle outside the cell and allow to diffuse suitable molecule inside the cell.
- It bound the viscous fluid of the cell, hence it helps to maintaining the distinct composition of the cell.
- It is a large, centrally located spherical component of the cell bounded by nucleus membrane( double layer covering ) which are connected to endoplasmic reticulum.
- It control all the metabolic activities of the cell and regulate the cell cycle.
- It is also known as "HEADQUARTER OF THE CELL"
- Nucleus is discovered by Robert Brown in 1831.
- It is well defined in case of eukaryote organisms while well defined nucleus is absent in case of prokaryotes.
- Component of the nucleus are, nucleolus and chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are also known as chromatin material which is thread like structure, it consist of DNA which carries hereditary information from parents to their offspring.
Function
The main function of the nucleus is are as follows:- It controls all the metabolic activities of the cell.
- It regulates the cell cycle.
- It helps in transmission of hereditary characters from parents to their off springs.
- The viscous jelly like fluid bounded by cell membrane where all organelle are freely suspended.
- It is discovered by Kolliker in1862.
1. Cytosol: The aqueous soluble part which contain protein forming cytoskeleton.
2. cell organelle: Living part of the cell having definite shape, structure and function eg. Mitochondria, Lysosomes, Nucleus, Ribosomes, etc.
Cell wall
- It is the outermost covering of the plant cells.
- It is absent in animal cells.
- It is made up of cellulose and pectin.
- Cell walls of two adjacent cells are joined by a layer called middle lamellae.
The main function of cell wall is following:
- It provides strength to the cell.
- It provide definite shape & size to the plant cell.
- It is semi permeable in nature, hence it allows to diffuse the molecules of different size outside & inside the cell.
- It is double membrane structure made up of protein and lipids where inner membrane folded inside to form cristae.
- Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, they provide energy to the cell by performing cellular respiration.
- Note: mitochondria absent in prokaryotes it is also absent in mammalian RBCs .
- It is first observed by Kolliker in insect cell.
- The main function of the mitochondria is are as follows:
- It is a site of energy synthesising.
- energy synthesise by mitochondria is stored in the form of ATP i.e Adenosine triphosphate
- it provide energy for cellular respiration eg. kreb cycle.
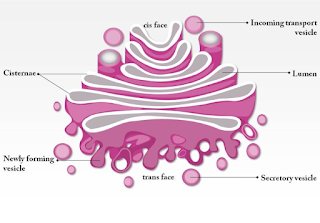
- It is discovered by camilo Golgi.
- It is a group of membrane bounded vesicles arrange parallel to each other in a stacks called cisternae.
- Golgi apparatus arises due to smooth endoplasmic reticulum i.e SER.
- Note: Golgi apparatus is absent in prokaryotes and mammalian RBCs
The main function of Golgi apparatus is are as follows:
- As the Golgi apparatus consists of vacuoles of secretory cells hence it secret the following:
- It help in the formation of lipids.
- It help in the formation of middle lamellae of the cell.
- The lipids and proteins synthesis by Golgi apparatus is stored in vacuole of endoplasmic reticulum at Golgi complex.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum is the network of membrane present in the cytoplasm.
- It is discovered by Portar, Claude and Fullam.
- ( Note: Endoplasmic reticulum is absent in procaryotes and Mammalian RBCs. )
1. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
2. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Qus4. Write the difference between SER & RER?
Ans: SER (Smooth endoplasmic reticulum)
- SER located near the cell membrane mainly made up of tubules.
- Ribosomes are absent.
- Help in membrane biogenesis.
- It also help in steroid, lipids and polysaccharides formation.
- It is located near the nucleus mainly made up of cisternae.
- Ribosomes are present.
- Mainly help in protein synthesising.
- Ans: Endoplasmic reticulum is the only organ which can move within a cell so it serve as a channel for the transportation of materials between various regions of cytoplasm and between cytoplasm and nucleus.
- It form endoskeleton of the cell.
- It help in the formation of fat, steroid, cholesterol, etc.
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum play a crucial role in detoxification of drugs and poisonous.
Ans: Membrane biogenesis is the process of synthesising cell membrane with the help of proteins and lipids. Endoplasmic reticulum(SER) is responsible for the synthesis of these membranes.
Ribosomes
- It is made up of RNA( ribonuclic acid ) and proteins molecules.
- Ribosomes are present (synthesised) in the nucleolus part because it is rich in RNA & proteins molecules also nucleolus is referred as the Factory of ribosomes.
- They are present in both animal and plant cell.
Function
The main function of ribosomes are as follows:- Ribosomes are the main sites of proteins synthesis.
- It synthesis all types of protein, proteins synthesised by ribosomes is stored in endoplasmic reticulum.
- It is tiny single layer sac-like granules, containing enzymes of intracellular digestion.
- It is also known as suicidal bag(digestive bag) of the cell.
- They do not have a definite shape and size.
- Note: Lysosome mainly occur in animal cell and few plant cell.
Function
The main function of lysosomes is are as follows:
- They remove the poorly working cell organelle from the cell by digesting them.
- They also destroy foreign particles when enter into the cell like bacteria and virus
Qus7.why lyososomes are called suicidal bag?( FAQs)
Ans: Because during metabolisms process cells get damaged and stop the metabolism process hence the lysosome break and release the hormone which digest their own dead cells. So it is called as Suicidal bag.
This process is referred as autolysis or self digestion.
Qus8. Defined the term autolysis?
Ans: It is defined as the process through which cell is destroyed by the action of its own enzymes.
Qus9. why lysosomes are called as digestive bag?
Ans: Because, they destroy the foreign materials such as bacteria and viruses when enter into the cell they digest them and protects the cell from viral and bacterial infection.
Vacuoles
- It is membrane bounded food storage part of the cell
- They are bounded by a outermost single membrane called Tonoplast.
- It is smaller in animal cell while larger in plant cell.
The main function of vacuoles are as follows:
- Vacuole help in maintaining osmotic pressure inside the cell.
- In plant cell it stored food & toxic metabolic product.
- It is double membrane generally dis like coiled structure, found only in plant cell.
- They have their own DNA & ribosomes and self replicating materials.
- They are colour pigments of the plant cell.
1.Leucoplast (white, found in underground parts)
2.Chromoplast(red, brown)
3.Chloroplast(Green in colour, found in aerial parts of plants & helps in photosynthesising. So it is called as the "kitchen of the plants")
Function
The main function of plastid are the following:
- Chromoplast( It provide colour to the plants)
- Chloroplast(It helps in photosynthesis)
- Leucoplast(It stored the food inside the plants in the form of starch, fats & proteins.
Qus10. How transportation of molecule done across the plasma membrane? Explain.
Ans: The transportation of molecules across the plasma membrane is done in the following ways:
1.Diffusion
2.Osmosis1.Diffusion
Diffusion
It is defined as the movement of solute(ions) particles from its high concentration to lower concentration is called diffusion.
- It occurs in any medium i.e solid, liquid & gas.
- Diffusion require no energy hence it is called as passive transport.
- It is unidirectional.
- Example. breathing, diffusion of gases in air.
Osmosis
It is defined as the movement of solute(ions) particles from its high concentration to lower concentration through Semi permeable membrane is called as osmosis.
It occurs only in liquid medium.
Osmosis require energy.
It is bidirectional.
Example. Movement of water in plant.
The movement of osmosis is two types:
1.Endomosis: The movement of solute/solvent particles from outside the cell to inside the cell is called as endomosis.
2.Exomosis: The movement of solute particles from inside to outside the cell is callesd as exomosis.
Qus11.Discuss the type of solution on the basis of concentration?
Ans: Types of solution on the basis of concentration
1.Isotonic solution
It occurs when the concentration of the solution is equal to the concentration of the cell. Due to this, no change will occur in the cell.
Isotonic solution: concentration of solution = concentration of the cell.
Result: No change will observe in the shape of the cell.
2.Hypertonic solution
It occur when the Concentration of the solution is greater than the concentration of the cell cytoplasm. Due to this, cell will shrink.
Hypertonic solution: Concentration of solution > Cell concentration
Result: Cell get shrink or
3.Hypotonic solution
It occurs when the concentration of the solution is lower than the concentration of the cell cytoplasm. As the result, cell swell up and may be burst.
Hypotonic solution: Concentration of solution < cell concentration.
Result: Cell will swells up & may be brust.
Qus12.What do you mean by plasmolysed cell?
Ans: Plasmolysed cell means, cell which get shrink due to the looses of water. It occur when cell is kept in a hypertonic solution in which the concentration of the solution is greater than the concentration of cell cytoplasm.
Qus13. What will happened when a eukaryotic cell is placed in a isotonic, hypertonic & hypotonic solution respectively?
Ans: When a eukaryotic cell is kept in isotonic solution, their is no changes will observed on the cell.
But cell will swells up when it kept in hypotonic solution and it may bursts.
similarly when is kept in hypertonic solution it will looses the water molecules and gets plasmolysed.
Reference taken from : NCERT BOOK and P S verma and P K Aggarwal
Image coppied from: Google image.
।। Radhe Radhe ।।
please comment your suggestion on
email and comment box:
Emai: murari9810658298@gmail.com
kumarghanshyam640@gmail.com






















Nice post! I have also written a article on this topic. Visit
ReplyDeletehttps://www.karareports.com/2020/01/cbse-notes-on-the-fundamental-unit-of-life.html
nice
ReplyDeleteThe distinctions made between unicellular and multicellular organisms, as well as the differences between plant and animal cells, are particularly helpful for students grappling with these concepts. For students aiming to deepen their understanding of cell biology, enrolling in biology tuition can be highly beneficial. A structured tuition program offers personalized guidance, interactive learning experiences, and access to a wealth of resources, all of which can solidify one's grasp of complex topics like cell structure and function.
ReplyDelete